Blacksmith: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Glanz (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Glanz (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (4 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
{{:MOOCit - | {{:MOOCit - Oben}} | ||
[[Datei:Flagge_Deutschland_MOOC_it_Kopie.png|70px|center|link=Schmied]] | [[Datei:Flagge_Deutschland_MOOC_it_Kopie.png|70px|center|link=Schmied]] | ||
[[Datei:Flagge_United_Kingdom_GB_MOOC_it.png|70px|center|link=Blacksmith]] | [[Datei:Flagge_United_Kingdom_GB_MOOC_it.png|70px|center|link=Blacksmith]] | ||
{| align=center | {| align=center | ||
{{:D-Tab}} | {{:D-Tab}} | ||
'''[[Blacksmithing]]''' | '''[[Blacksmithing]]''' | ||
{{o}} [[Bronze Age]] | |||
{{o}} [[Anvil]] | |||
{{o}} [[Forge]] | {{o}} [[Forge]] | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Farrier]] | ||
{{o}} [[Artistic Blacksmith]] | |||
{{o}} [[Bladesmith]] | |||
{{o}} [[Industrial Revolution]] | |||
{{o}} [[Metallurgy]] | |||
|} | |||
= Introduction = | |||
Welcome to your aiMOOC on the topic of '''[[Blacksmithing|blacksmithing]]'''! In this course, you will explore the ancient and fascinating craft of forging metal – from its early history to modern-day artistic applications. A [[blacksmith]] is not just a historical figure, but also a skilled modern craftsman working with precision, strength, and creativity. | |||
You will learn which [[tools]] are used in a traditional and modern [[smithy]], understand the key [[forging]] techniques, and discover the role of blacksmiths throughout history — from the [[Bronze Age]] through the [[Middle Ages]] to the [[Industrial Revolution]] and beyond. Interactive elements like quizzes, creative assignments, and digital media will guide and engage you in this hands-on profession. | |||
[[Datei:Blacksmith at work.jpg|1000px|rahmenlos|zentriert]] | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
= History of Blacksmithing = | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Origins and Development == | |||
The beginnings of [[blacksmithing]] trace back to the [[Bronze Age]], when humans started crafting weapons, tools, and ornaments from metal. A major leap came during the [[Iron Age]], when [[iron]] began replacing softer materials like [[bronze]], revolutionizing the craft. | |||
{{o}} [[Bronze Age]] | |||
{{o}} [[Iron Age]] | |||
{{o}} [[Ancient Metallurgy]] | |||
During the [[Middle Ages]], the [[village blacksmith]] was a central figure in every community. He created everything from horseshoes to weapons, and tools to door hinges. In towns, [[guilds]] regulated the craft, and skills were often passed down through families. | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Industrial Revolution and Transformation == | |||
The [[Industrial Revolution]] in the 19th century changed everything. Machines started replacing traditional forging methods. But blacksmithing evolved: [[industrial forges]] emerged, focusing on large parts for engines, railways, and construction. | |||
Today, blacksmiths specialize in: | |||
{{o}} [[Artistic blacksmithing]] | |||
{{o}} [[Toolsmithing]] | |||
{{o}} [[Bladesmithing]] | |||
{{o}} [[Farriery]] | {{o}} [[Farriery]] | ||
{{:BRK}} | |||
= Tools and Materials = | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Essential Tools == | |||
A blacksmith uses various [[tools]] to shape metal: | |||
{{o}} [[Anvil]] – a heavy block used as a work surface | |||
{{o}} [[Hammer]] – different types for striking and shaping | |||
{{o}} [[Tongs]] – to safely hold hot metal | |||
{{o}} [[Forge fire]] – used to heat metal up to 1000°C | |||
{{o}} [[Forge hearth]] – the fire pit where heating takes place | |||
Other common tools include chisels, files, vices, water tanks (for quenching), and modern equipment like power hammers and grinders. | |||
== | {{:BRK}} | ||
== Materials == | |||
The main material for blacksmithing is [[steel]], a refined form of [[iron]]. Depending on the project, blacksmiths may also use [[bronze]], [[copper]], or [[aluminum]]. | |||
= | {{:BRK}} | ||
= Blacksmithing Professions = | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
{{ | == Farrier == | ||
A [[farrier]] makes and fits [[horseshoes]], combining knowledge of forging with an understanding of [[equine anatomy]]. | |||
== | {{:BRK}} | ||
== Artistic Blacksmith == | |||
[[Artistic blacksmiths]] create gates, sculptures, chandeliers, and railings – blending craftsmanship with [[art and design]]. | |||
== | {{:BRK}} | ||
== Bladesmith == | |||
A [[bladesmith]] specializes in forging blades such as [[swords]], [[knives]], and [[axes]]. This work requires deep knowledge of [[heat treatment]], [[steel alloys]], and sharpening. | |||
= | {{:BRK}} | ||
= Modern Blacksmithing = | |||
Today, blacksmithing is making a comeback through [[craft markets]], [[DIY culture]], and [[YouTube]] channels. Modern [[bladesmiths]] and [[artisans]] are using both ancient techniques and new tools to create handmade goods that are functional and artistic. | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
= Interactive Tasks = | = Interactive Tasks = | ||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Quiz: Test Your Knowledge == | == Quiz: Test Your Knowledge == | ||
{{:Multiple-Choice Anfang}} | |||
''' | '''When did blacksmithing begin?''' | ||
( | (Bronze Age) | ||
(! | (!Stone Age) | ||
(! | (!Middle Ages) | ||
(! | (!Industrial Era) | ||
'''Which tool | '''Which of the following is NOT a blacksmithing tool?''' | ||
( | (Saw) | ||
(!Anvil) | (!Anvil) | ||
(!Hammer) | (!Hammer) | ||
(!Tongs) | |||
'''What is an anvil?''' | |||
(A solid surface used for metal shaping) | |||
(!A device for welding) | |||
(!A furnace for melting metal) | |||
(!A cooling tank) | |||
'''How hot can the forge get?''' | |||
(Over 1000°C) | |||
(!200°C) | |||
(!400°C max) | |||
(!Never over 800°C) | |||
''' | '''Who works primarily with horses?''' | ||
( | (Farrier) | ||
(! | (!Artistic blacksmith) | ||
(! | (!Toolsmith) | ||
(! | (!Bladesmith) | ||
''' | '''What is a "forge hearth"?''' | ||
( | (The fire pit used to heat metal) | ||
(! | (!A smoothing tool) | ||
(! | (!A grinding wheel) | ||
(! | (!A filing machine) | ||
'''What | '''What does an artistic blacksmith create?''' | ||
( | (Decorative metalwork) | ||
(! | (!Engines) | ||
(! | (!Machine tools) | ||
(! | (!Vehicles) | ||
'''What | '''What does a bladesmith make?''' | ||
( | (Swords and knives) | ||
(! | (!Horseshoes) | ||
(! | (!Chains) | ||
(! | (!Nails) | ||
''' | '''What era brought large-scale industrial forging?''' | ||
( | (19th century) | ||
(! | (!17th century) | ||
(! | (!Middle Ages) | ||
(! | (!21st century) | ||
'''Which | '''Which of these is not a typical blacksmithing material?''' | ||
( | (Plastic) | ||
(! | (!Steel) | ||
(! | (!Bronze) | ||
(! | (!Copper) | ||
{{:Multiple-Choice Ende}} | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Memory == | == Memory == | ||
<div class="memo-quiz"> | <div class="memo-quiz"> | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Anvil || Solid surface for shaping metal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Forge || Fire used to heat metal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Farrier || Works with horse hooves | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Artistic Blacksmith || Creates decorative metalwork | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bronze Age || Start of blacksmithing | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{:Memo | {{:Memo Ende}} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Drag and Drop == | |||
<div class="lueckentext-quiz"> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Match the correct terms. | |||
! Topic | |||
|- | |||
| '''Bronze Age''' | |||
| Beginning of metal forging | |||
|- | |||
| '''Anvil''' | |||
| Blacksmith’s work surface | |||
|- | |||
| '''Farrier''' | |||
| Shoeing horses | |||
|- | |||
| '''Forge''' | |||
| Heats the metal | |||
|- | |||
| '''Steel''' | |||
| Main material for forging | |||
|} | |||
</div> | |||
<br> | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Crossword Puzzle == | == Crossword Puzzle == | ||
<div class="kreuzwort-quiz"> | <div class="kreuzwort-quiz"> | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Anvil || | | Anvil || Solid base for blacksmithing | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Forge || Fire area for heating metal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Hammer || Primary tool for striking | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bronze || First forged metal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Farrier || Expert for horseshoes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Art || Blacksmithing as creative expression | |||
|} | |} | ||
{{: | {{:Kreuzwort Ende}} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== | {{:BRK}} | ||
{{: | == LearningApps == | ||
{'''Complete the text.''' | <iframe> https://learningapps.org/index.php?s=Blacksmithing </iframe> | ||
{{:BRK}} | |||
== Cloze Test == | |||
<quiz display=simple> | |||
{'''Complete the text.'''<br> | |||
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
Blacksmithing began during the { Bronze Age } and evolved through the [[Iron Age]]. | |||
{{ | An [[anvil]] serves as a { solid } work surface. | ||
The [[forge hearth]] is the { fire } area of a blacksmith shop. | |||
A [[farrier]] specializes in { horseshoes }. | |||
An [[artistic blacksmith]] creates { decorative } objects from metal. | |||
</quiz> | |||
= Open | <br> | ||
= Open Assignments = | |||
=== Easy === | === Easy === | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Tool Sketching]]: Draw and label the most important tools used by a blacksmith (e.g., anvil, tongs, hammer). | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Craft Timeline]]: Create a timeline showing the key milestones in the history of blacksmithing. | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Daily Routine]]: Describe the daily routine of a medieval blacksmith in a short text. | ||
=== Standard === | === Standard === | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Interview a Blacksmith]]: Interview a local blacksmith (or watch an online interview) and summarize the insights gained. | ||
{{o}} [[Write a | {{o}} [[Compare Specializations]]: Compare the work of a farrier, bladesmith, and artistic blacksmith. | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Forge Report]]: Write a report about a modern forge, including tools, safety equipment, and typical projects. | ||
=== Advanced === | |||
{{o}} [[Build a Model Forge]]: Design and construct a model of a blacksmith’s forge using cardboard, clay, or digital tools. | |||
{{o}} [[Create a Documentary]]: Produce a short video documentary about the history and significance of blacksmithing. | |||
{{o}} [[Research Paper]]: Write a research paper on the transformation of the blacksmith’s role from ancient to modern times. | |||
{{:Offene Aufgabe - MOOC erstellen}} | |||
{{ | |||
{{: | {{:BRK}} | ||
= Learning Assessment = | |||
{{o}} [[Compare Eras]]: How did the blacksmith’s role differ between the Middle Ages and the Industrial Era? | |||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Skills Analysis]]: What skills are essential for an artistic blacksmith today, and how do they differ from those of a traditional blacksmith? | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Social Role]]: What was the social importance of a blacksmith in a medieval village? | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Material Science]]: Why is steel preferred over bronze in modern blacksmithing? | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Cultural Comparison]]: Explore how blacksmithing traditions differ across cultures (e.g., Japan, Africa, Europe). | ||
{{o}} [[ | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
= OERs on the Topic = | = OERs on the Topic = | ||
<iframe> https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blacksmith </iframe> | <iframe> https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blacksmith </iframe> | ||
{{:BRK}} | |||
{{:BRK}} | |||
= Links = | = Links = | ||
{| align=center | {| align=center | ||
{{:D-Tab}} | {{:D-Tab}} | ||
'''[[Blacksmithing]]''' | '''[[Blacksmithing]]''' | ||
{{o}} [[Bronze Age]] | |||
{{o}} [[Anvil]] | |||
{{o}} [[Forge]] | {{o}} [[Forge]] | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Farrier]] | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Artistic Blacksmith]] | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Bladesmith]] | ||
{{o}} [[ | {{o}} [[Industrial Revolution]] | ||
{{o}} [[Metallurgy]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:History]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Craftsmanship]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Engineering]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Artisanry]] | ||
= Share | = Share – Discuss – Evaluate = | ||
{{: | {{:Teilen - MOOCit}} | ||
[[Category:AI_MOOC]] [[Category: | [[Category:AI_MOOC]] [[Category:GPT aiMOOC]] [[Category:Blacksmithing]] [[Category:Vocational Education]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 5. Mai 2025, 10:28 Uhr


Blacksmith


Introduction
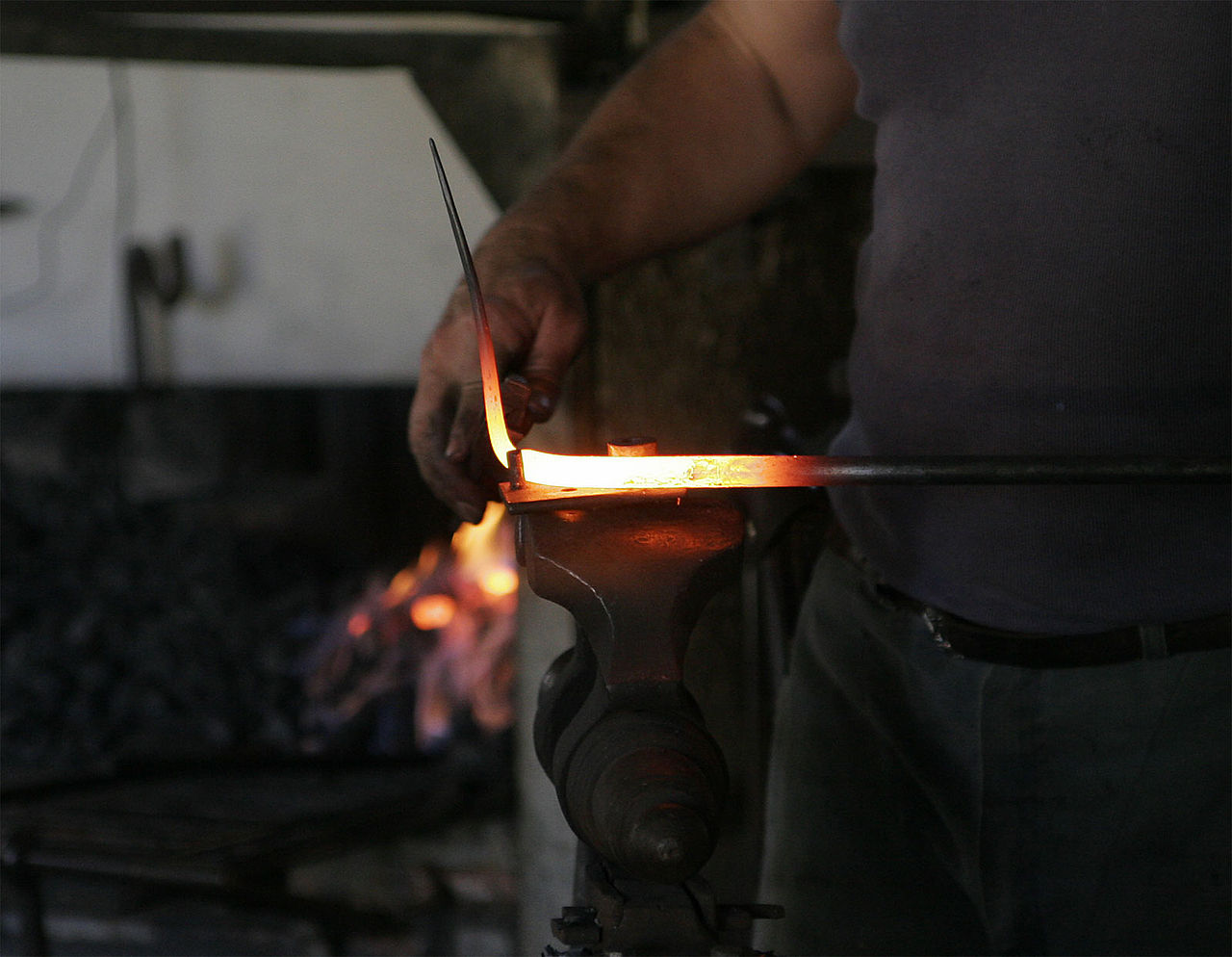
Welcome to your aiMOOC on the topic of blacksmithing! In this course, you will explore the ancient and fascinating craft of forging metal – from its early history to modern-day artistic applications. A blacksmith is not just a historical figure, but also a skilled modern craftsman working with precision, strength, and creativity.
You will learn which tools are used in a traditional and modern smithy, understand the key forging techniques, and discover the role of blacksmiths throughout history — from the Bronze Age through the Middle Ages to the Industrial Revolution and beyond. Interactive elements like quizzes, creative assignments, and digital media will guide and engage you in this hands-on profession.

History of Blacksmithing
Origins and Development
The beginnings of blacksmithing trace back to the Bronze Age, when humans started crafting weapons, tools, and ornaments from metal. A major leap came during the Iron Age, when iron began replacing softer materials like bronze, revolutionizing the craft.
During the Middle Ages, the village blacksmith was a central figure in every community. He created everything from horseshoes to weapons, and tools to door hinges. In towns, guilds regulated the craft, and skills were often passed down through families.
Industrial Revolution and Transformation
The Industrial Revolution in the 19th century changed everything. Machines started replacing traditional forging methods. But blacksmithing evolved: industrial forges emerged, focusing on large parts for engines, railways, and construction.
Today, blacksmiths specialize in:
Tools and Materials
Essential Tools
A blacksmith uses various tools to shape metal:
- Anvil – a heavy block used as a work surface
- Hammer – different types for striking and shaping
- Tongs – to safely hold hot metal
- Forge fire – used to heat metal up to 1000°C
- Forge hearth – the fire pit where heating takes place
Other common tools include chisels, files, vices, water tanks (for quenching), and modern equipment like power hammers and grinders.
Materials
The main material for blacksmithing is steel, a refined form of iron. Depending on the project, blacksmiths may also use bronze, copper, or aluminum.
Blacksmithing Professions
Farrier
A farrier makes and fits horseshoes, combining knowledge of forging with an understanding of equine anatomy.
Artistic Blacksmith
Artistic blacksmiths create gates, sculptures, chandeliers, and railings – blending craftsmanship with art and design.
Bladesmith
A bladesmith specializes in forging blades such as swords, knives, and axes. This work requires deep knowledge of heat treatment, steel alloys, and sharpening.
Modern Blacksmithing
Today, blacksmithing is making a comeback through craft markets, DIY culture, and YouTube channels. Modern bladesmiths and artisans are using both ancient techniques and new tools to create handmade goods that are functional and artistic.
Interactive Tasks
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
When did blacksmithing begin? (Bronze Age) (!Stone Age) (!Middle Ages) (!Industrial Era)
Which of the following is NOT a blacksmithing tool? (Saw) (!Anvil) (!Hammer) (!Tongs)
What is an anvil? (A solid surface used for metal shaping) (!A device for welding) (!A furnace for melting metal) (!A cooling tank)
How hot can the forge get? (Over 1000°C) (!200°C) (!400°C max) (!Never over 800°C)
Who works primarily with horses? (Farrier) (!Artistic blacksmith) (!Toolsmith) (!Bladesmith)
What is a "forge hearth"? (The fire pit used to heat metal) (!A smoothing tool) (!A grinding wheel) (!A filing machine)
What does an artistic blacksmith create? (Decorative metalwork) (!Engines) (!Machine tools) (!Vehicles)
What does a bladesmith make? (Swords and knives) (!Horseshoes) (!Chains) (!Nails)
What era brought large-scale industrial forging? (19th century) (!17th century) (!Middle Ages) (!21st century)
Which of these is not a typical blacksmithing material? (Plastic) (!Steel) (!Bronze) (!Copper)
Memory
| Anvil | Solid surface for shaping metal |
| Forge | Fire used to heat metal |
| Farrier | Works with horse hooves |
| Artistic Blacksmith | Creates decorative metalwork |
| Bronze Age | Start of blacksmithing |
Drag and Drop
| Match the correct terms. | Topic |
|---|---|
| Bronze Age | Beginning of metal forging |
| Anvil | Blacksmith’s work surface |
| Farrier | Shoeing horses |
| Forge | Heats the metal |
| Steel | Main material for forging |
Crossword Puzzle
| Anvil | Solid base for blacksmithing |
| Forge | Fire area for heating metal |
| Hammer | Primary tool for striking |
| Bronze | First forged metal |
| Farrier | Expert for horseshoes |
| Art | Blacksmithing as creative expression |
LearningApps
Cloze Test
Open Assignments
Easy
- Tool Sketching: Draw and label the most important tools used by a blacksmith (e.g., anvil, tongs, hammer).
- Craft Timeline: Create a timeline showing the key milestones in the history of blacksmithing.
- Daily Routine: Describe the daily routine of a medieval blacksmith in a short text.
Standard
- Interview a Blacksmith: Interview a local blacksmith (or watch an online interview) and summarize the insights gained.
- Compare Specializations: Compare the work of a farrier, bladesmith, and artistic blacksmith.
- Forge Report: Write a report about a modern forge, including tools, safety equipment, and typical projects.
Advanced
- Build a Model Forge: Design and construct a model of a blacksmith’s forge using cardboard, clay, or digital tools.
- Create a Documentary: Produce a short video documentary about the history and significance of blacksmithing.
- Research Paper: Write a research paper on the transformation of the blacksmith’s role from ancient to modern times.

Learning Assessment
- Compare Eras: How did the blacksmith’s role differ between the Middle Ages and the Industrial Era?
- Skills Analysis: What skills are essential for an artistic blacksmith today, and how do they differ from those of a traditional blacksmith?
- Social Role: What was the social importance of a blacksmith in a medieval village?
- Material Science: Why is steel preferred over bronze in modern blacksmithing?
- Cultural Comparison: Explore how blacksmithing traditions differ across cultures (e.g., Japan, Africa, Europe).
OERs on the Topic
Links
Share – Discuss – Evaluate
Schulfach+


aiMOOCs



aiMOOC Projekte


YouTube Music: THE MONKEY DANCE
Spotify: THE MONKEY DANCE
Apple Music: THE MONKEY DANCE

Amazon Music: THE MONKEY DANCE

The Monkey Dance SpreadShirtShop

|
|
|


Children for a better world >> Förderung der AI Fair-Image Challenge
Fair-Image wird von CHILDREN JUGEND HILFT! gefördert und ist mit der deutschlandweiten AI Fair-Image Challenge SIEGERPROJEKT 2025. Alle Infos zur Challenge hier >>. Infos zum Camp25 gibt es hier. Wenn auch Ihr Euch ehrenamtlich engagiert und noch finanzielle Unterstützung für Eurer Projekt braucht, dann stellt gerne einen Antrag bei JUGEND HILFT.